In this IG Live, we speak to Dr. Ajit Gokhale, the founder of Natural Solutions, India to discuss ‘Building Reed-bed system for Wastewater Management’.
Over our conversation, we get into details about the components of a Reed bed system, how the water purification is carried out, and the right methods of implementation. We also debunk common misconceptions about reed beds such as odor and maintenance requirements. Finally, we speak about the different types of flowering and fruiting plants that can be used for reed bed systems in Goa and along the Western Ghats.
Natural Solutions aims to spread environmental literacy and offers sustainable solutions for Urban as well as Rural Problems of water scarcity, Solid Waste Management, and wastewater treatment. Here are some key takeaways from our conversation.
Debunked myths about reed-bed systems
A reed bed system does not smell if designed correctly. The simple precaution of introducing the inlet pipe at the bottom of the reed bed and not the top of the ensures that no foul smell is emanated.
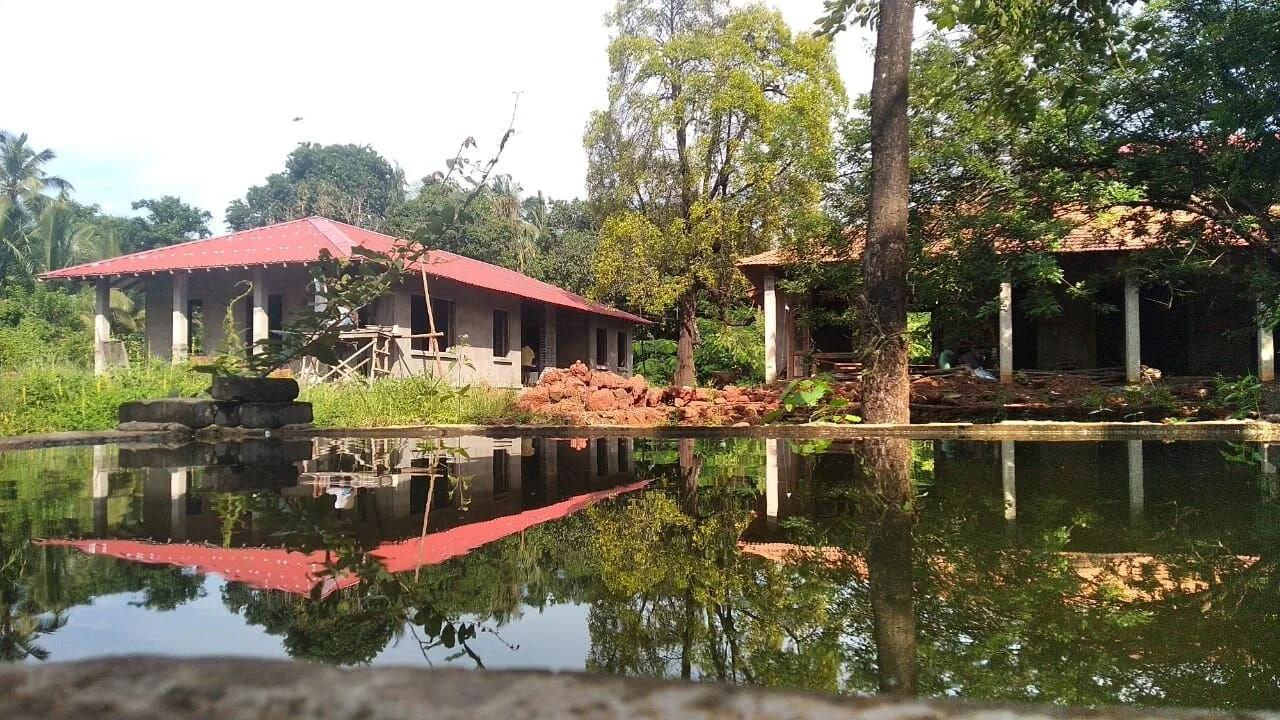
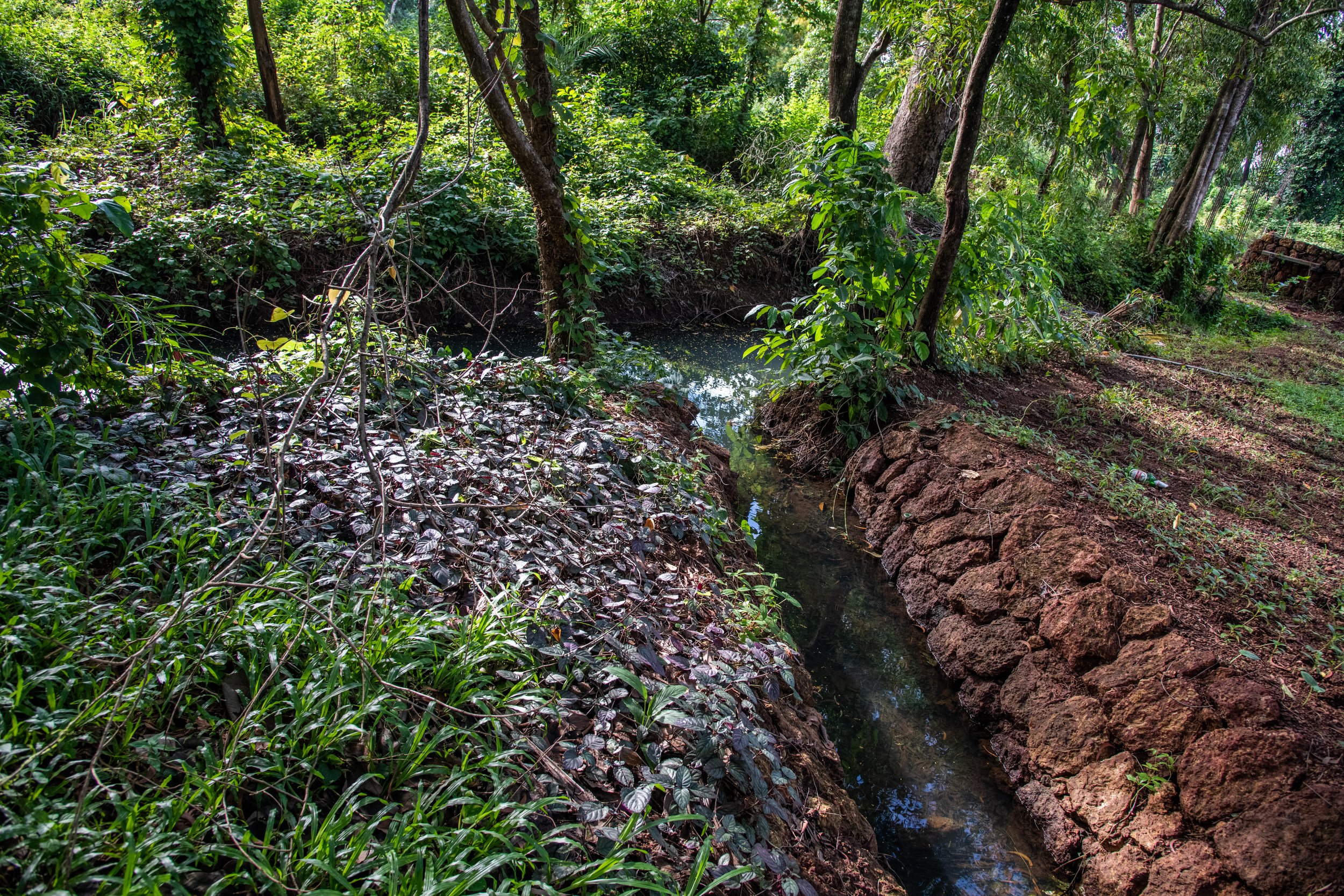
A reed bed does not have to be designed in a segregated area. It can very much designed as part of the landscape to be a walkable, usable space that can be accessed regularly.
A reed bed can be used to effectively purify not just greywater but also black water and industrial wastewater when implemented correctly. It does not require significant additional maintenance.
Maintaining a reed-bed system
A reed bed system typically consists of two parts - a sedimentation system (a septic tank/ an anaerobic digester/ Jalrakshak) and a filtration system (the reed bed itself). The entire system requires very little external care or maintenance.
As with any common drainage or waste treatment system, the septic tank/ anaerobic digester/ Jalrakshak has to be cleaned occasionally.
The reed bed itself does not require any maintenance. The plants can be trimmed for aesthetic value but it is not necessary. Trimming does not hamper the reed bed system as long as it is done as per a pruning schedule. Care has to be taken that the base of the plants are intact.
Benefits of a reed-bed system
A reed bed system is a one-time investment with lifelong benefits. It is extremely low maintenance in the long run.
Depending on the microclimate, the reed bed can purify every 1L of impure water to create 0.7 to 0.9L of filtered water that can be reused.
The filtered water can be reused for irrigation & gardening, washing cars, and for flushing.
The reed bed can be integrated as an accessible part of the landscape of the house with flowering and fruiting plants and trees that become home to local biodiversity.
Reed beds are sustainable, scalable, cost-effective ecologically engineered systems that can effectively purify wastewater. They are easy to maintain and can be designed into the landscape irrespective of the project size or typology.