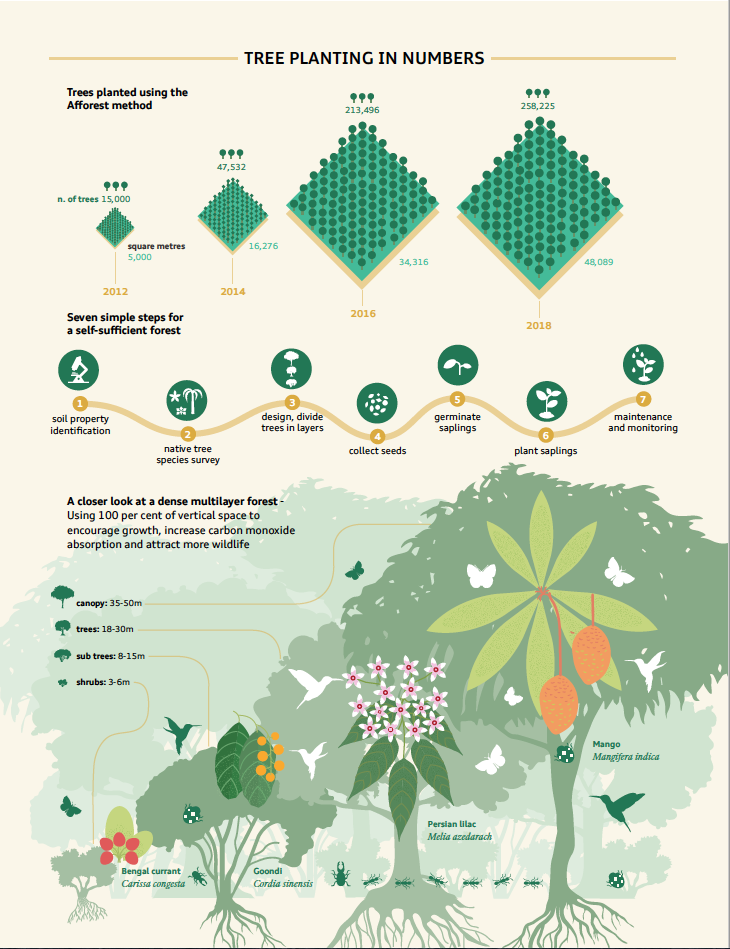
In this session, we speak to Shubhendu Sharma, Founder of Afforestt. Afforestt does amazing work rewilding barren land in rural as well as urban areas, in different climatic zones, using different species through a process called the Miyawaki Method. Over the conversation, we discuss the fundamentals of the Miyawaki technique, the how tos of growing a forest, the benefits of picking native species, the ways and means of making forests and landscapes in the cities, as well as the challenges of growing and maintaining a dense forest. We also delve into the subject of mono-planting and understand how it impacts local biodiversity.
Here are some key takeaways from the session:
Above ground, we perceive the forest as multiple trees, plants, and shrubs. But below ground, the forest grows as a single organism. ‘The Hidden Life of Trees’ by Peter Wohlleben is a great read to understand how trees grow and communicate
‘Jungle Trees of Central India’ by Pradip Krishen is an excellent resource to learn about Indian native trees.
One can visit the following native forests in India to find clues about and study the local indigenous species:
Sanjay Gandhi National Park in Mumbai
Kabini Forest in Bangalore
Srisailam Reserve in Hyderabad
Annamalai Forest in Tamil Nadu
Ridge Forest of the Aravalli Range in Delhi
Alwar Forest in Gurgaon and Haryana
Kanha and Tadoba National Parks in Central India
Jhilli Milli Forest in Kolkata
Jhalana Forest in Jaipur
Bathinda Forest in Punjab
Nepli Forest in Chandigarh
Afforestt also has an open source DIY toolkit on How To Build Forests. You can find the methodology here.
Read more about growing urban forests using the Miyawaki method in our introductory blogpost.